2.6 KiB
(IJCAI'25) RePST: Language Model Empowered Spatio-Temporal Forecasting via Semantic-Oriented Reprogramming
🙋 Please let us know if you find out a mistake or have any suggestions!
🐝 The full version of this paper can be accessed at https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.14505.
🌟 If you find this resource helpful, please consider to star this repository and cite our research:
@inproceedings{wang2025repst,
title={RePST: Language Model Empowered Spatio-Temporal Forecasting via Semantic-Oriented Reprogramming},
author={Wang, Hao and Han, Jindong and Fan, Wei and Sun, Leilei and Liu, Hao},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 34th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
year={2025}
}
Introduction
This repository contains the implementation of REPST, a framework for spatio-temporal forecasting that leverages the reasoning and generalization capabilities of Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs). REPST utilizes a semantic-aware spatio-temporal decomposer and selective discrete reprogramming to enable PLMs to handle complex spatio-temporal data, especially in data-scarce environments.
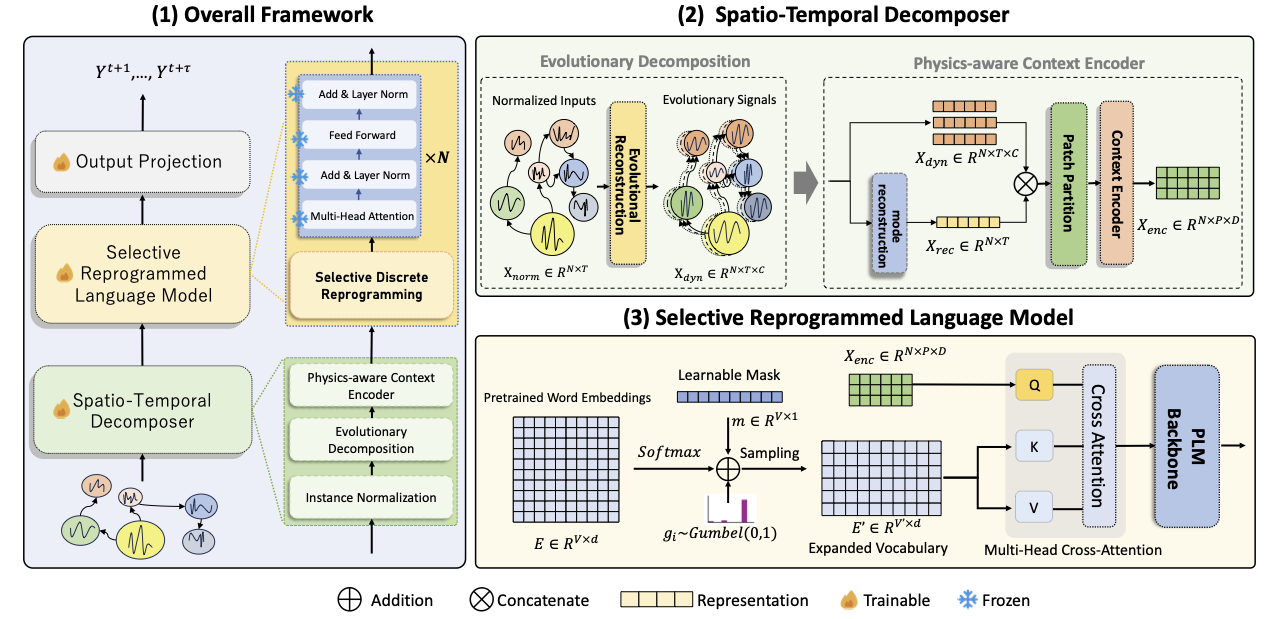
- RePST comprises two key components: (1) a dynamic mode decomposition approach that disentangles spatially correlated time series into interpretable components, and (2) an expanded spatio-temporal vocabulary that helps PLMs better understand the dynamics of complex spatio-temporal systems, to guide PLM reasoning.

Requirements
Use python 3.11 from MiniConda
- torch==2.0.1
- accelerate==0.28.0
- einops==0.6.0
- matplotlib==3.7.0
- numpy==1.24.4
- pandas==2.1.4
- scikit_learn==1.3.2
- scipy==1.11.4
- tqdm==4.66.1
- transformers==4.36.2
To install all dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Datasets
Pending
You can access the well pre-processed datasets from [Google Drive], then place the downloaded contents under ./dataset
Detailed usage
Please refer to run.py for the detailed description of each hyperparameter.
Acknowledgement
Our baseline model implementation adapts BasicTS as the code base and have extensively modified it to our purposes. We thank the authors for sharing their implementations and related resources.